Abstract
The quality characteristics of herbal medicines and herbal preparations are important factors to consider when evaluating the quality of medicinal products. All elements that either directly or indirectly impact the product's acceptability, efficacy, and safety contribute to its overall quality. However, naturopathy is challenging due to the absence of standards. There are no guidelines on the management and processing of raw materials and production of finished products. Appropriate GMP guidelines must be followed to ensure the effectiveness, safety and quality of herbal medicines for daily use.
Keywords
Quality Control, Herbal Drug, Medicinal plant, GMP
Introduction
The quality of herbal drugs and their formulations is the sum of all factors that affect their safety, efficacy, and acceptability. Some quality aspects of herbal drugs include:
- Standardization: There is a lack of standardization for raw materials, processing methods, finished products, and dosage formulations.
- Quality control: There is a lack of quality control criteria. Contamination: Herbal drugs can be contaminated by molds, insects, animal excreta, toxic metals, and pesticides
- Adulteration: Herbal drugs can be adulterated or misidentified.
- Ingredient complexity: The ingredients in herbal drugs can be complex and non-uniform.
Herbal drugs are prepared by subjecting Erbel drugs to treatments such as extraction, distillation, expression, fractionation, purification, concentration, or fermentation.
QUALITY ASPECT OF HERBAL DRUG AND ITS FORMULATION:
The quality aspects of herbal remedies and herbal formulations must be considered when assessing the quality of pharmaceuticals. The quality of herbal medicines is the sum of all factors that either directly or indirectly impact the product's safety, effectiveness, and acceptability.
TYPES:
The quality of herbal drugs and their formulations is important for their safety, effectiveness, and acceptability. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Adulterants: Herbal products can be deliberately adulterated with toxic plants, heavy metals, steroids, and other substances.
- Elemental content: The elemental composition of medicinal herbs should be analysed to ensure they don't contain harmful levels of elements.
- Standardization: Standardization of herbal formulations is essential for quality control.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors like sunlight, rain, temperature, soil, and storage conditions can cause significant variation in the quality of herbal products.
- Physicochemical properties: The organoleptic and physicochemical properties of a plant material or its extracts can affect the choice of its formulation.
- Active principles: The active principles in herbal products can be known or unknown.
TESTING:
Quality aspects of herbal drugs and their formulations are assessed through a variety of tests and methods, including:
- Raw material evaluation: The quality of the herbs used in the product is assessed.
- Microscopy: The powdered herbal drug is examined under a microscope.
- Chemical fingerprinting: This technique helps identify the active ingredients and marker compounds in the herbal medication.
- DNA testing: This technique provides scientific data for quality control.
- Heavy metal testing: This test is crucial for the safety and quality of herbal products.
- Sensory evaluation: The shape, size, color, texture, odor, and taste of the herbal drug are evaluated.
- Chromatographic, spectrophotometric, and
- Electrophoresis methods: These methods are used to standardize herbal drugs.
- Polarography: This method is used to standardize herbal drugs.
- Molecular biomarkers: These biomarkers are used in fingerprints to standardize herbal drugs.
- Good Manufacturing
- Practices (GMP) guidelines: These guidelines are essential to maintain product quality and protect consumer health.
- In-process testing: This involves performing quality tests at various stages of the manufacturing process.
- Contamination Control: This is a critical Aspect of herbal medication industries to ensure safety, product quality and environmental protection.
Quality aspect of herbal drug:
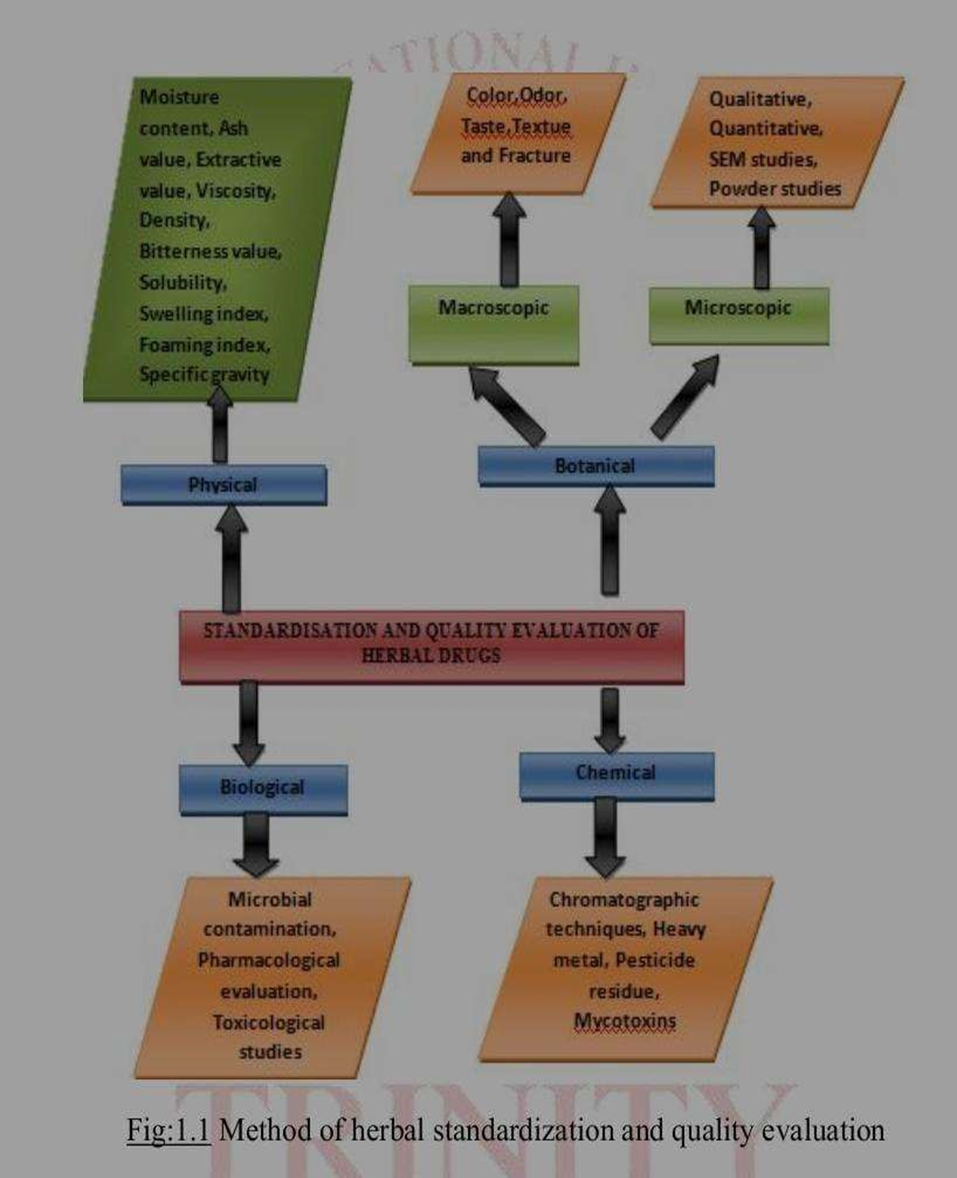
Fig 1: Method of Herbal standardization and Quality evaluation.

PRODUCED:
The quality of herbal drugs and their formulations is determined by many factors, including:
- Physical, chemical, and geographical aspects: These can all affect the quality of the herbals.
- Adulteration: This is an increasing concern for herbal material quality.
- Contamination: Herbal drugs can be contaminated with toxic metals, pesticides, microbes, and animal excreta.
- Ingredients: These can be internal factors that affect the quality of herbal drugs.
The quality of herbal drugs is assessed using a variety of methods, including:
Chemical and phytochemical tests: These are used to determine the quality of herbal drugs and their formulations.
Analytical techniques: These are used to determine the quality of herbal drugs and their formulations.
Macroscopic and microscopic evaluation: These methods are used to identify herbal drugs. Macroscopic evaluation involves visually inspecting the herbal drug for its colour, odour, size, and shape.

REGULATED:
The quality of herbal drugs and their formulations is regulated by the Department of AYUSH and the D and C Act. The D and C Act controls the following aspects of herbal drugs:
formulation composition, manufacture, labelling, packing, quality, and export.
The quality of herbal drugs is determined by their identity, purity, content, and other chemical, physical, or biological properties. The quality of herbal drugs can be affected by internal and external factors:
- Internal factors: Complexity and non-uniformity of the ingredients
- External factors: Contamination by toxic metals, pesticides residues, and microbes, adulteration, and misidentification.
To ensure the quality of herbal drugs, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the following quality control methods:
- Macroscopic and microscopic examination
- Ensuring that the medicinal plant materials are free from visible signs of contamination
- Ensuring that there are no abnormalities, discoloration, slime, or signs of deterioration.
- Standardisation process that involves prescribing a set of standards to ensure the quality, efficacy, safety and reproducibility of herbal medicines. Standardisation helps healthcare professionals prescribe treatments with confidence.

Application of Chromatography for the evaluation of Herbal drug and Formulation:
Withania somnifera, widely referred to as Ashwagandha, is a multifaceted herb that is integral to both traditional and contemporary herbal medicine. This plant, part of the Solanacee family, occupies an important role in the traditions of India and other regions. Ashwagandha is known for its possible therapeutic benefits, encompassing adaptogenic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and stress relieving effects. Additionally, it has become noteworthy in the pharmaceutical and dietary supplement sectors because of its numerous health advantages. The quality and genuineness of Ashwagandha products can be affected by multiple factors, such as the cultivation source, processing techniques, and storage environments.
This precious herb is, nonetheless, susceptible to possible adulteration and contamination, which could jeopardize its effectiveness and safety. To maintain the purity and quality of Ashwagandha formulations, it is crucial to create analytical techniques that can identify adulteration in these products. HPTLC has become a useful resource in this context, providing an economical and effective method for separating and examining intricate combinations of chemical substances. HPTLC provides a quick, economical, and effective technique for dentifying pure Ashwagandha BRM from possible adulterants in Ashwagandha items present in the market, enhancing the overall integrity and trustworthiness of herbal products in the sector. This technique conserves time and resources by allowing the analysis of several samples at once on a single plate, reducing both solvent usage and waste generation. It acts as an essential quality assurance method, confirming the authenticity and purity of Ashwagandha products, which in turn boosts consumer confidence and supports the reputation of the herbal sector.
ADVANTAGES:
- Here are the major benefits of using herbal medicine.
- Cost effective and accessible. High quality herbs should always be taken in controlled dosages as prescribed by a qualified naturopath.
- Natural healing.
- Mitigated risk of side effects.
- You can safely test and try different herbs.
DISADVANTAGE
The primary constraints are the absence of formulation for raw materials, processing techniques, and final goods, dose formulation, and the absence of quality control standards.
FUTURE PERSPECTIVE:
Some ways to improve the quality of herbal drugs include:
desired therapeutic effects consistently
- Heavy metal testing: Heavy metal testing can help ensure the quality and safety of herbal products.
- Microscopy: Microscopy can be used to identify herbal crude materials.
- Choralography and get photometric method
- Molecular biomarkers: Molecular biomarkers can be used in fingerprints to standardize herbal drugs.
REGULATORY GUIDELINES
Good agricultural and collection practices (GACP):
These guidelines help ensure the quality of the raw materials used in herbal products.
Good laboratory/manufacturing practices (GLP/GMP):
These guidelines help ensure that the manufacturing processes are robust and standardized.
CONCLUSION
Aspects of quality that relate to procedures used to preserve the efficacy or safety of medications. To investigate the various facets of the abundant herbal drugs and herbal remedies. Herbal medications are becoming more and more well-liked globally, He cause of the rise in usage, safety concerns are more significant. There are two types of quality problems with herbal medications: internal and external. External problems like adulteration, misidentification, and contamination (such as hazardous metals, pesticide residues, and microorganisms) are covered in detail in this review. A dosage form called an herbal drug formulation is made up of one or more herbs or processed herb(s) in predetermined amounts to offer nutritional cosmetic. and other benefits intended for use in the diagnosis, treatment, mitigation, or other uses of diseases in humans or animals. This report included a thorough analysis of WHO GMP and GLP guidelines.
REFERENCE
- Jiwan p. Lavande, Sanjay k. Bais, Avinash Siddharam Gurav Review on Quality aspects of herbal drugs and its formulations. International journal of pharmaceutical research and application; 2023; (8) 1993-1205.
- Aruna M. Garud, Dr. Varsha M. Jadhav, Dr.Vilasrao J. Kadam; A Review Chromatographic analytical phytopharmaceuticals, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences; 2017; 174-178.
- Vi-Zang Liang, Peishan Xie, Kelvin Chan, Quality control of herbal medicines, Journal of chromatography B: 2004, 53-70
- Junhua Zhang, Barbara Wider. Hongcai Shang. Xuemei Li. Edzard Ernst. Quality of herbal medicines: Challenges and solutions, Elevier health journal (2011) 101-105.
- Mingzhe Xu, Baobin Huang, Luli Li, Wenya: Assessment of Adulterated Traditional Chinese Medicines in China: 2014: (8), 1-8.
- Thillaivanam. S. Samraj. K. A Review on Challenges, Constraints and Opportunities in Herbal Medicine, International Journal of Herbal Medicine: 2014; (2), 21-24
- Dilip Ghosh. Quality Issues of Herbal Medicines: Internal and External Factors, International Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medicine; 2018. (11), 67-69.
- Md. Shant Mollah, Mohammad Abu bin Nyeem: A review on quality control and evaluation of herbal drugs in modern ent, International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021, (6), 9-13
- Shulammithi R. Sharanya M. Tejaswim R. Kiranmai M. Standardization and quality evaluation of herbal drug, IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences; 2016, (11), 1-10.
- Prashant Yadav, Kanhiya Mahour and Ashok Kumar, Standardization and Journal of Advanced Laboratory Research in Biology. 2011; (2), 162-166 Evaluation of 1 Herbal Drug Formulations,
- Humanal very e20 string Practic or Medicinal Producte
- Dr. Kuntal Das, Good Manufacturing Practices, Textbook of herbal drug technology, Nirali Prakashan; 2022; (2): 13.2-13.19.
- K.Sahira Banu and De L. Cathrine: General Techniques Involved in Phytochemical Analysis, International Journal of Advanced Research in Chemical Science (JARCS), 2015: (2), 1-8
- Anna M. Gand. De Varsha M. Jadhav, Dr. Vilastao 1. Kadain; A Review Chromatographic analytical phytopharmaceuticals, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences; 2017: 174-178
- Kshirsagar Diksha Prakash. Dr. Vipul Patel, Dr. Rasika bhalke. Karale Pradip Rohidas, Gaikwad Sayali, A review on current quality control methods for standardization of herbal drugs, International Journal of Pharmaceutics and Drug Analysis: 2017: (5), 1-7.


 Vaibhav Pujari*
Vaibhav Pujari*




 10.5281/zenodo.14365794
10.5281/zenodo.14365794