Abstract
The objectives of the present investigation was to formulate and evaluate Ramipril Microspheres by using different polymers such as HPMC K-4M, HPMCK-15M, HPMCK-100M and Ethyl Cellulose. The shape of microspheres were characterized by optical microspheres and surface morphology evaluated by scanning electron microscopy. Other evolutionary parameters such as Entrapment efficiency, Buoyancy study, In-vitro study was studied. The buoyancy study compliances the floating behavior of microspheres. In-vitro study shows prolonged sustained release pattern of drug release. Scanning electron microscopy showed that microspheres surface was sponge like structure with porous in nature. The prepared Floating microspheres of Ramipril might be used for prolonged drug relese in GIT, for better drug action and improved patient compliance.
Keywords
Ramipril, Microspheres, Scanning electron microscopy, Entrapment efficiency, Buoyancy study, In-vitro drug release, Sustained drug release
Introduction
Floating microsphere are gastro- retentive drug delivery system. As the system floats over gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at desired rate resulting in increased gastric retention time. Floating system are low density that have sufficiently bouncy to float over gastric fluid. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. Attempts are being made to develop a drug delivery system which can be provide therapeutically effective plasma drug concentration for longer period thereby reducing the frequency and minimizing fluctuation in plasma drug concentration at steady state by delivering the drug in a sustained manner.
MATERIAL AND METHOD MATARIAL
Ramipril is used as active pharmaceutical ingredients, HPMC K-4M, HPMC K-15M, HPMC K-100M, Ethyl Cellulose, Sodium alginate, Calcium chloride are of standard grade.
Table 01: Formula for Ramipril microspheres
|
Ingredients (mg)
|
F1
|
F2
|
F3
|
F4
|
F5
|
F6
|
F7
|
F8
|
F9
|
|
Ramipril
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
|
HPMC K -4M
|
30
|
50
|
70
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
|
HPMC K -15M
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
30
|
50
|
70
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
|
HPMC K -100M
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
30
|
50
|
70
|
|
Ethyl cellulose
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
10
|
|
Sodium alginate
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
3000
|
|
Calcium chloride
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
2000
|
U.V Scanning:
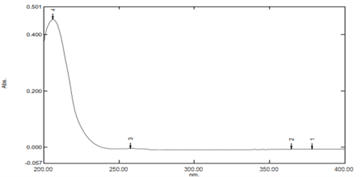
Figure No. 01: UV spectrum of Ramipril
? max of was found to be 206 nm in 1.2 acidic buffer of PH 1.2. Hence further study was carried out at 206 nm in pH 1.2 acidic buffer.
Standard calibration curves:
Table 02: Calibration curves in 0.1 N HCL
|
Sr.no.
|
Concentration (µg/ml)
|
Absorbance
|
|
1
|
00
|
00
|
|
2
|
02
|
0.096
|
|
3
|
04
|
0.180
|
|
4
|
06
|
0.268
|
|
5
|
08
|
0.365
|
|
6
|
10
|
0.447
|
|
7
|
12
|
0.540
|
|
8
|
14
|
0.643
|
|
9
|
16
|
0.719
|
|
10
|
18
|
0.818
|
|
11
|
20
|
0.916
|
|
12
|
22
|
1.035
|
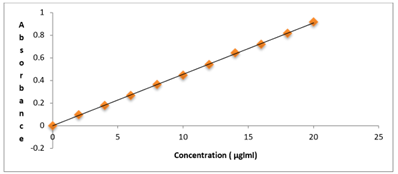
Figure No.02: Calibration curve of Ramipril in 0.1 N HCl
DSC:
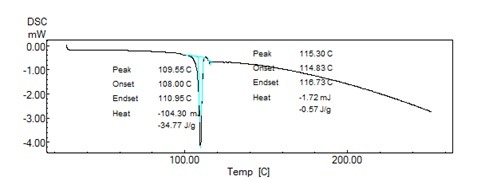
Figure No. 03: DSC of pure drug Ramipril
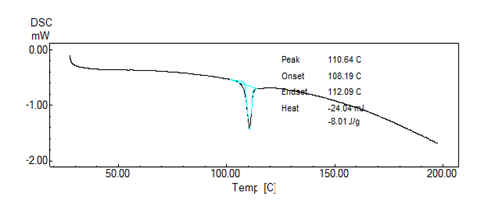
Figure No. 04: DSC of formulation
DSC Thermograms of pure Ramipril, blend of polymer with drug were determined. Pure Ramipril showed a sharp onset of peak at 109o C corresponding to its melting point. There was no appreciable change in the melting endotherms of physical mixture compared to that of pure drug Ramipril. Absence of any new endothermic peak or disappearance or shit of endothermic peak confirms that there is no any interaction and hence the polymers are compatible with drug.
SEM:
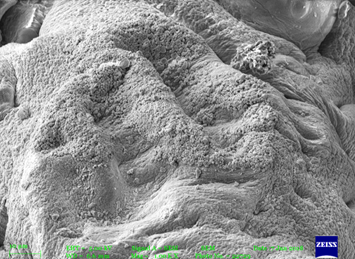
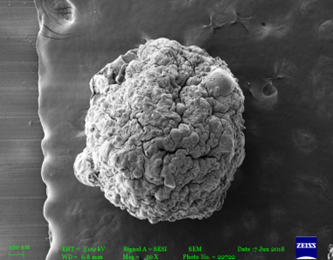
Figure No. 05: Figures of SEM of Microspheres
The microspheres were spherical and the external surface was smooth with slightly rough surface which could be due to drying. The internal surface of microspheres showed sponge like nature.
Evaluation Of Floating Microspheres For Floating Parameters:
Table 03: %Yield, mean particle size, angle of repose of microspheres
|
Formulation code
|
% yield
|
Mean particle size
|
Angle of repose
|
|
F1
|
92.83 ± 0.275
|
820 ± 1.520
|
26.12 ± 0.103
|
|
F2
|
94.43 ± 0.376
|
870 ± 1.007
|
28.07 ± 0.001
|
|
F3
|
90.23 ± 1.495
|
865 ± 2.065
|
19.65 ± 0.565
|
|
F4
|
82.10 ± 3.181
|
840 ± 3.105
|
12.95 ± 0.589
|
|
F5
|
88.63 ± 0.988
|
811 ± 4.187
|
16.52 ± 0.722
|
|
F6
|
89.88 ± 0.957
|
841 ± 0.174
|
16.12 ± 0.405
|
|
F7
|
95.75 ± 2.326
|
830 ± 5.0132
|
15.79 ± 0.400
|
|
F8
|
80.76 ± 0.668
|
865 ± 0.421
|
20.19 ± 0.182
|
|
F9
|
95.62 ± 0.490
|
841 ± 2.0174
|
16.59 ± 0.230
|
Table 04: entrapment efficiency, in vitro buoyancy, % drug release of ramipril microspheres
|
Formulation code
|
Entrapment efficiency
|
In-vitro buoyancy
|
% drug release
|
|
F1
|
89 ± 10.4
|
12+
|
85.74 ± 0.502
|
|
F2
|
85 ± 2.645
|
12+
|
80.31 ± 0.654
|
|
F3
|
85.66 ± 3.511
|
12+
|
82.41 ± 0.195
|
|
F4
|
83.66 ± 3.785
|
12+
|
86.04 ± 0.627
|
|
F5
|
86.66 ±1.527
|
12+
|
82.54 ± 0.401
|
|
F6
|
89.66 ± 21.45
|
12+
|
85.98 ± 0.598
|
|
F7
|
93.33 ± 0.577
|
12+
|
86.31 ± 0.185
|
|
F8
|
87 ± 15.099
|
12+
|
85.53 ± 0.697
|
|
F9
|
89.33 ± 9.865
|
12+
|
84.23 ± 2.081
|
Table 05: % Drug release study of ramipril microspheres (f1 –f5)
|
Time
( Hr )
|
% Release
|
|
F1
|
F2
|
F3
|
F4
|
F5
|
|
1
|
15.93 ± 0.109
|
22.57 ± 0.775
|
21.64 ± 0.775
|
21.64 ± 0.775
|
19.50 ± 1.216
|
|
2
|
27.36 ± 0.405
|
25.22 ± 0.995
|
25.22 ± 0.995
|
28.65 ± 1.028
|
31.70 ± 3.273
|
|
3
|
32.74 ± 0.334
|
36.45 ± 0.687
|
36.71 ± 0.687
|
36.71 ± 0.687
|
37.75 ± 0.401
|
|
4
|
37.94 ± 0.591
|
42.68 ± 0.385
|
42.88 ± 0.512
|
46.71 ± 0.687
|
42.22 ± 0.420
|
|
5
|
53.78 ± 0.975
|
52.69 ± 0.465
|
53 ± 0.675
|
54.62 ± 0.876
|
57.84 ± 0.450
|
|
6
|
60.62 ± 0.332
|
60.08 ± 0.681
|
59.88 ± 0.295
|
59.95 ± 0.225
|
59.89 ± 0.410
|
|
7
|
64.88 ± 0.327
|
64.06 ± 3.352
|
65.99 ± 0.687
|
63.65 ± 0.488
|
62.93 ± 1.276
|
|
8
|
70.27 ± 0.625
|
73.65 ± 0.390
|
75.07 ± 0.976
|
69.75 ± 0.700
|
73.87 ± 1.153
|
|
9
|
77.91 ± 0.226
|
77.57 ± 0.497
|
77.62 ± 0.845
|
77.47± 0.562
|
79.16 ± 0.405
|
|
10
|
79.29 ± 0.190
|
78.58 ± 0.594
|
80.72 ± 1.403
|
82.28 ± 1.460
|
81.31 ± 0.295
|
|
11
|
85.74 ± 0.502
|
80.31 ± 0.654
|
82.41 ± 0.195
|
86.04 ± 0.627
|
82.54 ± 0.401
|
Table 06: % drug release study of ramipril microspheres (f6 – f9)
|
Time
( Hr )
|
% Release
|
|
F6
|
F7
|
F8
|
F9
|
|
1
|
19.83 ± 1.476
|
19.37 ± 1.072
|
21.91 ± 0.436
|
14.24 ± 0.780
|
|
2
|
24.57 ± 0.334
|
28.87 ± 1.203
|
28.65 ± 1.028
|
28.01 ± 0.900
|
|
3
|
37.48 ± 0.788
|
37.23 ± 0.519
|
37.23 ± 0.519
|
34.63 ± 2.439
|
|
4
|
41.87 ± 1.842
|
43 ± 0.300
|
43 ± 0.300
|
37.81 ± 0.190
|
|
5
|
51.37 ± 1.106
|
51.37 ± 1.106
|
54.62 ± 0.876
|
58.65 ± 1.350
|
|
6
|
61.71 ± 1.240
|
60.02 ± 0.195
|
59.89 ± 0.127
|
60.65 ± 1.350
|
|
7
|
64.04 ± 1.105
|
63.65 ± 0.488
|
64.35 ± 0.872
|
64.43 ± 1.144
|
|
8
|
68.71 ± 0.709
|
69.03 ± 1.170
|
71.81 ± 3.366
|
68.90 ± 1.001
|
|
9
|
78.64 ± 0.790
|
77.49 ± 2.619
|
76.50 ± 0.957
|
79.81 ± 0.740
|
|
10
|
81.31 ± 0.225
|
82.34 ± 1.409
|
81.37 ± 0.295
|
83.77 ± 2.361
|
|
11
|
85.98 ± 0.598
|
86.31 ± 0.185
|
85.53 ± 0.697
|
84.23 ± 2.081
|

Figure No.06: % Release of drug of formulations (F-F3)
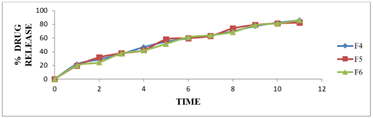
Figure No.07: % Release of drug of formulations (F4-F6)

Figure No. 08: % Release of drug of formulations (F7-F9)
Stability Study:
Stability study of optimized best batch F7 at temperature 40 ± 2oC and relative humidity 75 ± 5%
Table 07: Stability study of best batch
|
Sr. no.
|
Time
|
Appearance
|
% drug entrapment
|
Floating
|
% drug release
|
|
1
|
0
|
White
|
93.33 ± 0.577
|
12+
|
86.31 ± 0.185
|
|
2
|
30 days
|
White
|
92.69 ± 1.684
|
12+
|
86.5 ± 0.400
|
|
3
|
60 days
|
White
|
93.32 ± .0.912
|
12+
|
86.96 ± 0.550
|
|
4
|
90 days
|
White
|
93.41 ± 0.167
|
12+
|
86.78 ± 0.436
|
CONCLUSION
Microspheres of Ramipril can be successfully prepared using various polymers such as HPMC , Ethyl cellulose. The % yield of all microspheres formulation was more than 75% suggesting that method used for encapsulation was effective. Particle size of all formulation was in range of 810 to 870 µm. The entrapment efficiency was good in all batches. The in vitro buoyancy was after 12 hrs indicated satisfactory performance of proposed formulation. The flow properties of of all prepared microspheres were good as indicated. The good flow properties suggested that the microspheres produced were no aggregated. The % release microspheres were found to be order F7< F4>
REFERENCE
- Pandey N, Negi A, Mahara K, Formation and evaluation of floating Microspheres of Nateglinide. International Journal of Pharma Science and Research 2016;7(11):453-464.
- Kapoor D, Patel R, Formulation Optimization and evaluation of floating Microspheres of Captopril. Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Science 2012;2(9) 1-10.
- Gadad A, Naik S, Panchaxari M, Bolmal U, Formulation and evaluation of Gastrotrntive floating Microspheres of Lafutidine. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research 2016;50(2) 576-581.
- Gaythridevi M, Adlin J, Floating microspheres : A review. International Journal of Research and Chemistry 2016;6(3).504.
- Negi R, Microbaloons : A better approach for gastro retention. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research 2014;2(2) 100-107.
- Bansal H, Simar Preet Kaur, Microspheres : method of prepration and application a comparative study. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Review and Research 2011;10(1) 69-78.
- Kadam N, Suvarna V, Microspheres : A brief review. Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Science 2015; 5(47) 13-19..
- Metkari V, Kulkarni L, Patil P, Jadhav P, Bomane G, Kumbhar C, Microspheres – A new drug delivery system : a review. Journal of Current Pharma Research2014;4(2) 1128-1133.
- Ratnaparkhi M, Dhiwar S, Dhage K, Bhore S, Kadam P, Patil P, Formulation and invitro characterization of floating microspheres of Metformin HCl. Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2012;4(5) 1390-1400.


 Pawde Manik Sambhaji*
Pawde Manik Sambhaji*







 10.5281/zenodo.14571016
10.5281/zenodo.14571016